

Alternate Way: The other toArray() method.Covert ArrayList of strings to String array.Covert ArrayList of integers to int array.The returned array is not connected to ArrayList in any way, but keep in mind that it is a shallow copy of the elements of the ArrayList. So by passing an empty array (size 0), we’re forcing ArrayList to create a new array and return it. This was intentional because if we pass a non-empty array and it has enough room to fit all elements, ArrayList will use this array instead of creating a new one. Notice that we passed an empty array new Integer.
There is something else about the behavior of toArray(.) method you must understand.

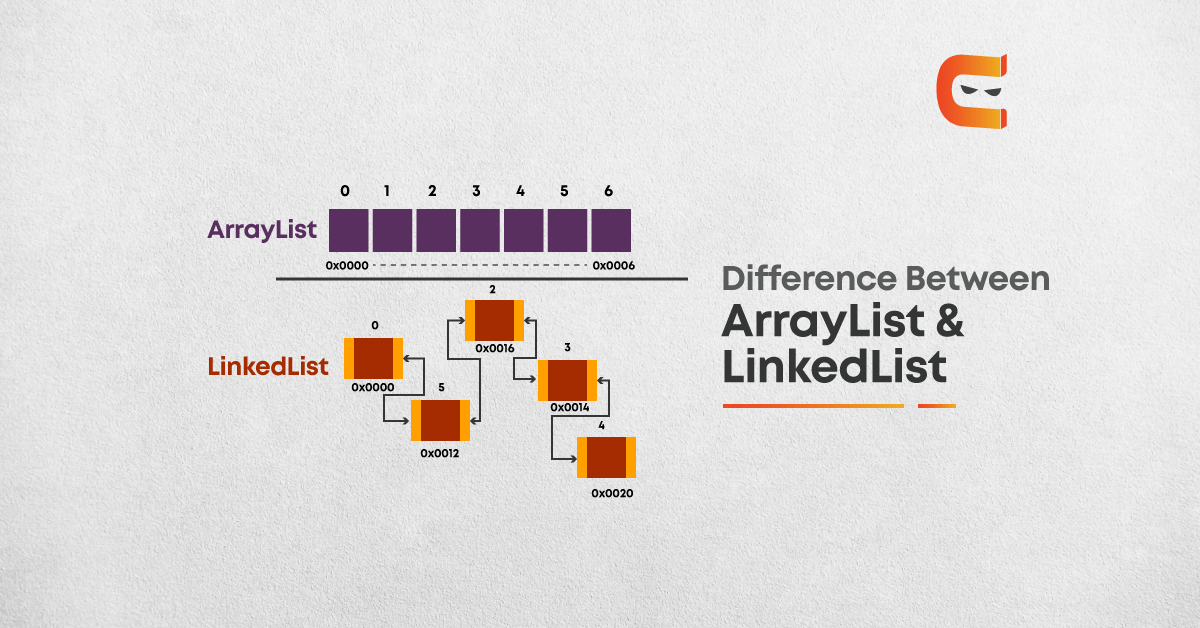
In other words, the toArray(.) method uses the type of the argument, Integer to create another array of the same type, places all elements from ArrayList into the array in order and returns it. What’s with the weird-looking argument new Integer? The reason it is there because the type of returned array is determined using this argument. String subjects = įollowing the above methods, we can now easily convert an array to ArrayList.String array = strList. The syntax of the Arrays.asList() is as below: ArrayList arraylist = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(arrayname)) Using Arrays.asList(), the array is passed to this method and a list object is obtained, which is again passed to the constructor of the ArrayList class as a parameter. Conversion of an Array to ArrayList Using Arrays.asList() Whereas, elements can be added or removed to/from ArrayList at any point due to its resizable nature. To add or remove elements to/from an array, we have to create a new list. The main difference between an array and ArrayList is that the length of an array cannot be modified or extended. Difference Between Array and ArrayList in Java The ArrayList is a resizable array that stores a dynamic collection of elements found within the java.util package. In this way, exhibit individuals are gotten to utilizing, while ArrayList has an arrangement of techniques to get to components and adjust them. ArrayList is a piece of collection framework in Java. A collections framework is a unified architecture for representing and manipulating collections, enabling collections to be manipulated independently of implementation details. Basically, an Array is fundamental usefulness gave by Java. A collection is an object that represents a group of objects. An array is the basic built-in functionality of Java. Differences Between Array and ArrayList in Java. The standard Collection class ArrayList extends the List interface. When an array is created using ArrayList, a dynamic array is created that can grow and shrink in size when needed. the array can not grow in size once it is created. After creation, the length of the array is fixed. The ArrayList overcomes the issue of a static array in standard Java i.e. Internally, a new array which is 1.5 times the size the original array is. For example, if we want to store the data of 50 books, we can create an array of the string type that can hold 50 books. ArrayList, the capacity of the underlying array grows 50 of its size each time.

What Is an Array in Java?Īn array is a collection of a fixed number of similar types of data. There are three different methods to convert an array to ArrayList in Java such as Arrays.asList(), Collections.addAll() and add().īefore proceeding with the demonstration, let us understand what is an array and ArrayList and how they differ from each other. This tutorial article will introduce different ways to create ArrayList from array in Java.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
